Fusion 360’s Additive Manufacturing Workspace
A Comprehensive Guide for Design Engineers and Manufacturing
The advent of additive manufacturing (AM) has transformed the way industries approach design, prototyping, and production.
Autodesk's Fusion 360 has emerged as a leading platform to streamline workflows for engineers and manufacturers, with its dedicated Additive Manufacturing Workspace offering a one-stop solution for 3D printing needs, helping design manufacturing to incorporate the 'Lean Manufacturing' methods into their workflow.
From designing for manufacturability to optimizing for performance, Fusion 360 provides tools to simplify complex tasks, ensuring precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
This guide delves deep into Fusion 360's Additive Manufacturing Workspace, explaining its features, capabilities, benefits, and practical applications, particularly for design engineers and manufacturing buyers who seek to harness its potential.
What Is Fusion 360’s Additive Manufacturing Workspace?
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based product design and manufacturing software that integrates various functionalities like CAD, CAM, CAE, and PCB design into one unified platform.
Its Additive Manufacturing Workspace focuses specifically on facilitating 3D printing workflows, enabling users to design, simulate, and prepare parts for additive manufacturing—all within the same environment.
Key highlights of the Additive Manufacturing Workspace include:
- Comprehensive support for multiple additive processes, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
- Automatic and customizable print preparation tools to streamline slicing, orientation, and support generation.
- Design optimization tailored to additive processes, incorporating lattice structures and topology optimization.
- Integrated simulation tools for stress analysis, thermal deformation, and more, reducing the trial-and-error approach in physical prototyping.
Why the Additive Manufacturing Workspace Matters
The manufacturing world is moving beyond traditional subtractive methods toward hybrid approaches that leverage both subtractive and additive manufacturing.
Fusion 360’s Additive Manufacturing Workspace empowers professionals to:
- Reduce lead times by preparing 3D-printed prototypes directly from the design stage.
- Enhance design freedom through complex geometries, lightweight structures, and customization options.
- Cut costs associated with material wastage and tooling.
- Collaborate seamlessly across teams, thanks to Fusion 360’s cloud infrastructure.
For design engineers and manufacturing buyers, these advantages translate into streamlined procurement, faster time-to-market, and improved product performance.
Features of Fusion 360’s Additive Manufacturing Workspace
1. Intuitive Model Preparation
The Additive Manufacturing Workspace simplifies the tedious process of preparing models for 3D printing. Its key preparation features include:
- Automatic Slicing: Fusion 360 automates slicing, converting 3D models into layers compatible with additive machines. Users can adjust layer heights and other slicing parameters.
- Orientation and Nesting: Proper part orientation is critical to achieving optimal mechanical properties and minimizing support structures. Fusion 360 suggests orientations to reduce build time and material usage.
- Support Structure Generation: The workspace automatically generates necessary supports based on overhang angles, with options for manual adjustments.
2. Lattice and Generative Design
Fusion 360 empowers users to integrate lattice structures and utilize generative design tools to reduce weight while maintaining strength. These capabilities are particularly beneficial for industries like aerospace and automotive, where material efficiency is paramount.
- Lattice Design: Use built-in templates or customize lattice parameters to create lightweight, high-strength parts.
- Topology Optimization: Generate organic, structurally optimized geometries tailored to the loads and constraints of the design.
3. Seamless Simulation Tools
The workspace includes simulation features to analyze how parts will behave during and after printing.
These simulations help predict:
- Thermal deformation during the printing process.
- Residual stresses that might lead to warping or cracking.
- Structural integrity of printed parts under operational loads.
4. Material-Specific Libraries
Fusion 360 includes extensive material libraries that cater to different additive manufacturing processes. Engineers can select materials based on thermal, mechanical, or chemical properties, ensuring compatibility with the final application.
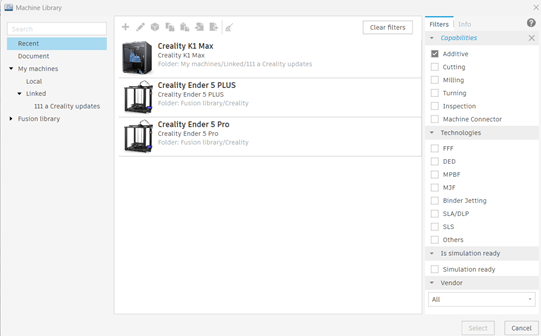
5. Machine Integration
Fusion 360 supports direct integration with a wide range of 3D printers, offering:
- Predefined machine profiles for ease of setup.
- Export options for standard file formats like G-code, STL, and 3MF.
- Compatibility with industrial machines from leading manufacturers, such as Stratasys, Ultimaker, and Formlabs.
6. Cloud Collaboration and Version Control
Thanks to Fusion 360's cloud architecture, multiple stakeholders can collaborate on a design, track changes, and access the latest files from any location. This is particularly valuable for teams managing complex projects or working remotely.

Applications of the Additive Manufacturing Workspace
The Additive Manufacturing Workspace is versatile enough to cater to various industries. Below are key application areas:
1. Rapid Prototyping
Fusion 360 reduces the time and cost involved in developing prototypes, allowing teams to iterate quickly. The ability to perform simulations before printing ensures that prototypes are functional and precise.
2. Tooling and Fixtures
The software is instrumental in creating custom jigs, fixtures, and tooling components. Additive manufacturing eliminates the need for expensive molds or machining, enabling rapid turnaround for production aids.
3. End-Use Parts
With advances in materials and additive technologies, Fusion 360 facilitates the production of low-volume, custom, or intricate parts that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
4. Reverse Engineering
The workspace integrates well with reverse engineering workflows, enabling users to scan existing parts, modify designs, and produce replicas or improved versions using 3D printing.
Step-by-Step Workflow in Fusion 360’s Additive Manufacturing Workspace
Here’s how to navigate the Additive Manufacturing Workspace to create a 3D-printed part:
Step 1: Design Creation
Begin by designing your part using Fusion 360’s robust CAD tools. Ensure the model is optimized for the intended printing process, accounting for features like overhangs and wall thickness.
Step 2: Prepare for Additive Manufacturing
- Switch to the Additive Manufacturing Workspace.
- Orient the part for optimal printability and mechanical performance.
- Generate and customize support structures.
Step 3: Simulation and Validation
Run simulations to predict thermal and structural issues. Adjust parameters as needed to reduce risks like warping or residual stress.
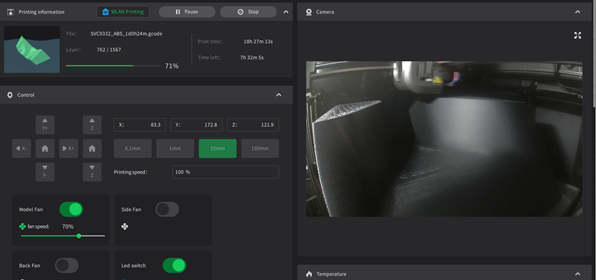
Step 4: Slice and Export
Finalize slicing settings and export the file in the required format for your 3D printer. Fusion 360 allows direct printer integration or manual file transfer.
Step 5: Printing and Post-Processing
Transfer the file to your printer, execute the print, and perform necessary post-processing steps like support removal or surface finishing.
Benefits for Design Engineers and Manufacturing
Fusion 360’s Additive Manufacturing Workspace offers distinct advantages tailored to the needs of professionals in the manufacturing domain:
1. Improved Efficiency
With an integrated workflow from design to printing, users can avoid time-consuming data transfers between separate software.
2. Enhanced Collaboration
The cloud-based infrastructure fosters real-time collaboration, enabling seamless communication between design teams and manufacturers.
3. Cost-Effective Solutions
By leveraging simulation and generative design, users can minimize material use and production errors, reducing overall costs.
4. Future-Proof Capabilities
Fusion 360 evolves with industry trends, incorporating new materials, processes, and technologies to keep users ahead of the curve.
Tips for Maximizing Fusion 360’s Additive Manufacturing Workspace
- Leverage Generative Design: Use it early in the design process to explore innovative solutions and save material.
- Understand Material Properties: Choose materials suited to the application’s requirements and the chosen AM process.
- Iterate Using Simulation: Don’t skip simulations; they can save time and cost by identifying potential issues upfront.
- Keep Learning: Autodesk regularly updates Fusion 360. Stay informed about new features to get the most out of the software.
Challenges and How Fusion 360 Addresses Them
Challenge 1: Complex Geometry
Designing complex parts can be time-consuming. Fusion 360 simplifies this with tools like parametric modeling, lattice structures, and topology optimization.
Challenge 2: Material Limitations
Not all 3D printing materials are suitable for every application. Fusion 360’s extensive material library and simulation tools ensure informed material choices.
Challenge 3: Printer Compatibility
The diversity of 3D printers can create compatibility issues. Fusion 360 bridges this gap with direct integrations and standard file formats.
The Future of Fusion 360 in Additive Manufacturing
Fusion 360 continues to innovate, with Autodesk investing in cutting-edge technologies like AI-driven design, advanced simulations, and hybrid manufacturing workflows.
As additive manufacturing becomes more integral to global supply chains, tools like Fusion 360 will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Fusion 360’s Additive Manufacturing Workspace is a game-changer for design engineers and manufacturing, offering an all-in-one solution for creating, optimizing, and producing 3D-printed parts.
By embracing its capabilities, professionals can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and unlock new possibilities in design and manufacturing.
Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or a manufacturing buyer exploring additive manufacturing for the first time, Fusion 360 provides the tools you need to succeed in a rapidly evolving industry.
Embrace the future of manufacturing today—because in the world of design, innovation waits for no one.